
INLINE FUSE FULL
CSA Canadian approval that guarantees the a fuse or fuse holder has been manufactured in full compliance with the CSA C22.2 No.UL recognition, c-UL Listing, c-UL Recognition, c-UL-us Listing and c-UL-us Recognition does not imply full compliance with UL-248-14. The UL Listing guarantees that a fuse has been manufactured in full compliance with the UL 248-14 standard.It also includes extra insulation and insulating barriers to prevent the presence of living conducting services during fuse change procedures.Īpprovals and ratings for fuse holders include UL, CSA, BSI, VED, IEC (UMF), SEMKO, and Dentori. The limited access fuse holder is built to necessitate the use of a tool (usually a screwdriver). However, some international equipment standards limit the degree of user accessibility to a fuse holder to reduce the risk of electrical shock to a non-technical user. Users of UL/CSA-compliant fuse holders are accustomed to a fuse carrier with a knurled cap that allows them to reach and change a fuse without the need for tools. Waterproofing, vibration resistance, and a blow fuse warning are all common features of fuse holders. Depending on the designer's objective and where they are situated, they can allow for both easy fuse replacement and make fuses more difficult to access. In-Line Fuse Holders – These wire-in, wire-out/line and load fuse holders are essentially self-contained wire harnesses that offer a wide range of application versatility. Panel Mount Fuse Holders – They are normally wire-in, wire-out/line, and load, and when installed appropriately, they can protect people from electrical risks when mounted through an enclosure or on a back plane of an enclosure. They usually need to be isolated and insulated from the environment, yet they have a wide range of applications. P CB Fuse Holders – Most cost-effective, with the lowest purchase cost but the fewest features. PCB Fuse Clips – Most cost-effective, with the lowest purchase cost but the fewest features. Furthermore, certain fuse holder models allow the fuse to be removed by hand, whereas others require the use of a specific tool.Įlectronic fuse holders are commonly classified into four types: Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Fuse Clips, Printed Circuit Board Fuse Holders, Panel Mount Fuse Holders, and In-Line Fuse Holders. To help prevent electrical damage, many fuses and fuse holders incorporate specific features that prevent fuses of the correct style but incorrect current rating from being put in the holder. A blade fuse, for example, will not fit in a cartridge fuse holder. A fuse holder's style and size are directly tied to the type and current rating of the fuse it is designed to retain. They are available in a variety of styles, each tailored to a certain fuse. Ⅰ Fuse holder basics 1.1 What is a Fuse Holder?Ī fuse holder, as the name implies, is a device that retains an electrical fuse. The article will direct you to the necessary information and dispel any doubts you may have. You'll have peace of mind knowing that your fuses are safely and continually protected in any commercial, industrial, or automobile application. Choose from a variety of clip, block, socket, and plug-on cap styles in a variety of amperages. Imperial has everything you need, including open and enclosed alternatives. A fuse is a type of safety device that protects an electrical circuit against overcurrent. A circuit breaker is an automated switch that stops the passage of electric current when it is rapidly overloaded or under extremely high stress. This safeguard is usually in the form of a circuit breaker or a fuse.
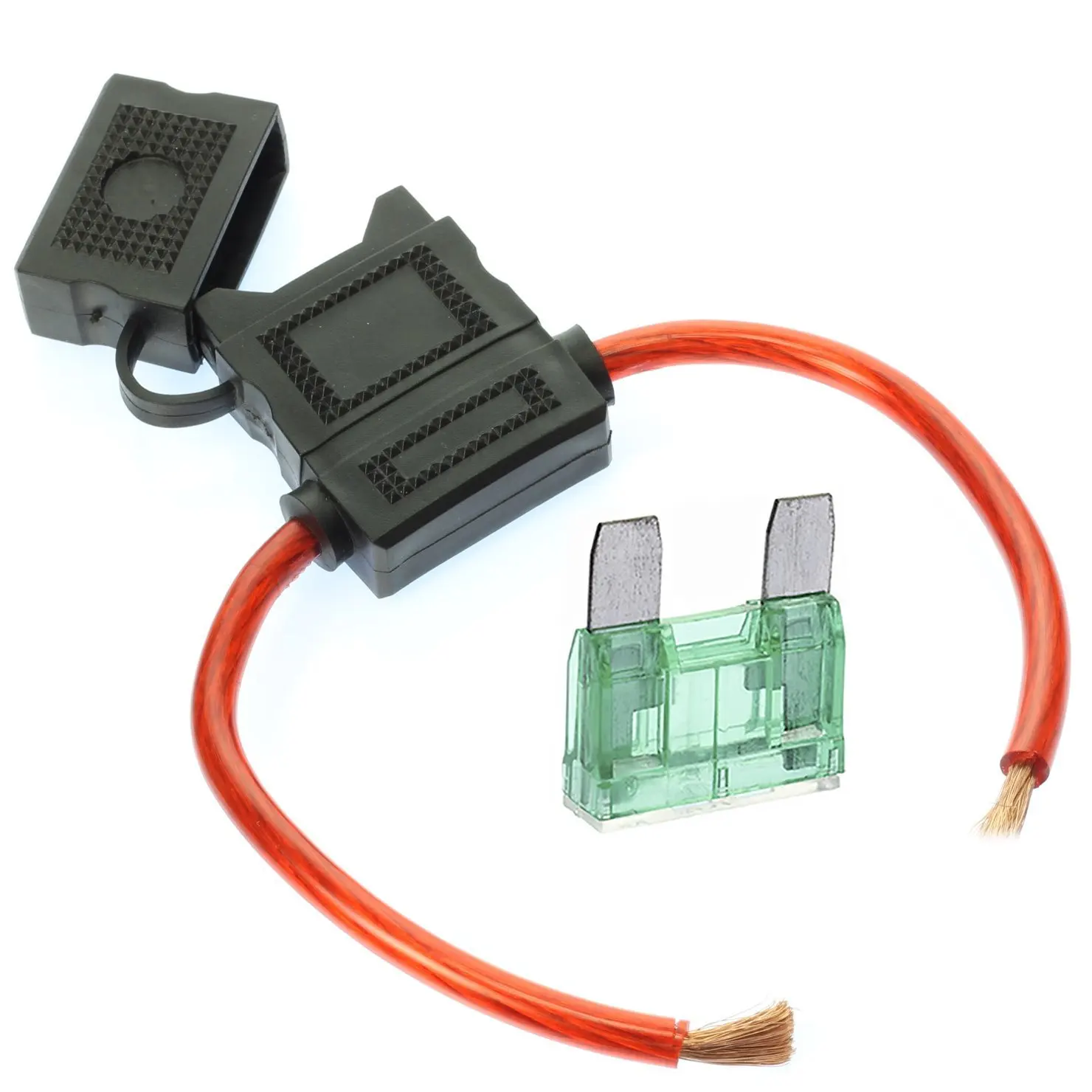
In the event of a circuit overload, the principal duty is to protect both the equipment and the equipment operator. Circuit protection is frequently included in electronic devices. Ⅶ Quality Industrial Fuse Products at Low Pricesįuse holders and blocks are simple components that provide a critical function: mounting, enclosing, and safeguarding electrical fuses. Ⅵ LED Blow Fuse Indicators/LED Fuse HoldersĦ.1 How Does an LED Blown Fuse Indicator Work? Ⅲ Fuse Blocks, Fuse Holders & Fuse Covers 1.4 Thermal Considerations of Fuses and Fuse Holdersġ.6 Design Strategies of Fuses and Fuse Holders


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
